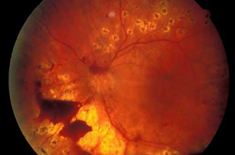
What is Vitreous hemorrhage?
Vitreous hemorrhage is the extravasation, or leakage, of blood into the areas in and around the vitreous humor of the eye. The vitreous humor is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eye. A variety of conditions can result in blood leaking into the vitreous humor, which can cause impaired vision, floaters, and photopsia.
What Causes it?
Damage to normal blood vessels
Retinal blood vessels that are damaged through injury or trauma can cause a vitreous haemorrhage. Some eye problems can also cause damage to the blood vessels of the retina, such as retinal detachment . A retinal vein occlusion can also cause vitreous haemorrhage, as it blocks the veins that feed the retina, which may then bleed into the vitreous ‘gel’.
Growth of abnormal blood vessels
Some eye conditions can cause the growth of abnormal blood vessels that bleed into the vitreous ‘gel’ of the eye. The later stages of diabetic retinopathy , some retinal vein occlusions , and occasionally wet ARMD can cause abnormal, delicate blood vessels to grow and bleed into the vitreous cavity.
Bleeding from other parts of the eye
Occasionally, blood from another source can cause a vitreous haemorrhage. While it is very rare, a haemorrhage in another part of the eye, or even a tumour, can cause blood to leak through into the vitreous ‘gel’.
Who are at risk?
Patients having injury or trauma,retinal detachment ,retinal vein occlusion ,diabetic retinopathy and wet ARMD are more risk of having vitreous hemorrhage.
What are the symptoms?
Common symptoms of vitreous hemorrhage include:
Blurry vision
Floaters- faint cobweb-like apparitions floating through the field of vision
Reddish tint to vision
Photopsia – brief flashes of light in the peripheral vision.
Small vitreous hemorrhage often manifests itself as "floaters". A moderate case will often result in dark streaks in the vision, while dense vitreous hemorrhage can significantly inhibit vision.
How is it diagnosed?
Vitreous hemorrhage is diagnosed by identifying symptoms, examining the eye, and performing tests to identify cause. Some common tests include:
- Examination of the eye with a microscope
- Pupil dilation and examination
- An ultrasound examination may be used if the doctor does not have a clear view of the back of the eye
- Blood tests to check for specific causes such as diabetes
- A CT scan to check for injury around the eye
- Referral to a retinal specialist.
What is the treatment?
The treatment method used depends on the cause of the hemorrhage. In most cases, the patient is advised to rest with the head elevated 30–45°, and sometimes to put patches over the eyes to limit movement prior to treatment in order to allow the blood to settle. The patient is also advised to avoid taking medications that cause blood thinning (such as aspirin or similar medications).
The goal of the treatment is to fix the cause of the hemorrhage as quickly as possible. Retinal tears are closed by Laser treatment or cryotherapy, and detached retinas are reattached surgically.
Even after treatment, it can take months for the body to clear all of the blood from the vitreous. In cases of vitreous hemorrhage due to detached retina,long-standing vitreous hemorrhage with a duration of more than 2–3 months, or cases associated with rubeosis iridis or glaucoma, a vitrectomy may be necessary to remove the standing blood in the vitreous.
For more information or to book appointment for Vitreous Hemorrhage Treatment in Prayagraj, please contact Dr. Ashish Mitra at +91 8085309909 or write us at info@eyeclinicprayagraj.com